 Starter Generators (ISG)
Starter Generators (ISG)
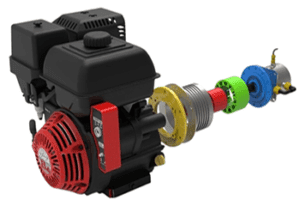
All of Innotec’s generators can be configured as starter generators. These include the engine mounted line of generators, pulley driven line of generators or direct shaft coupled units.
ISG Basics
ISGs are devices used to start an engine as well as act as a generator. The benefit of using this technology is that it removes the need for a separate starter motor to start up an engine, thus reducing components as well as reducing space usage. Starter generators serve the purpose of three components:
- Starter- to start up an engine
- Electric motor- to power AC, water pump, etc.
- Alternator- to recharge batteries
Depending on engine selection, the starter generator can be configured to fit with a minimal profile and reduce space compared to standard alternators.
Components of the ISG (integrated starter generator):
The main components include the stator/housing, rotor and controller(s). The generator may need specific sensors to work in starting or generating functions.
Stator
Rotor
Controller
Working:
While starting up an engine, the ISG unit receives energy from the battery. The stator receives energy from the battery and causes rotation of the rotor, which then cranks up the engine. After the engine starts, the crankshaft rotation causes the rotor to rotate, which produces an electric current in the stator and this electric energy is used to recharge the battery. Thus, ISG is a bi-directional power transfer system. Innotec’s generators can be used bi-directionally mechanically as well.
ISGs are used in HEVs (Hybrid electric vehicles) and MHEVs (Mild hybrid electric vehicles), as they result in reduced fuel consumption and improved performance. The most common variants include
24V ISG
48V Starter Generator
72V ISG
400V ISG
To control and manage the function of the ISG as a starter and a generator, a controller is used, which helps the ISG system communicate with the engine via hall effect sensors or sin/cos sensors. Various features of controller include:
Over-current protection
Over/under voltage shut-off
Temperature check
Communicating with the engine
Battery current control
Battery charging control
